NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Economics Chapter 5 Consumer Rights
Question 1: Why are rules and regulations required in the marketplace? Illustrate with a few examples.
Answer:
Rules and regulations are required in the market place due to the following reasons :
- The consumers are exploited by the shopkeepers and traders in different ways such as less weight or measurement, more price, adulterated and defective goods.
- In case of a complaint regarding a good or service, the shopkeeper or trader tries to avoid any responsibility. The seller tries to shift all the responsibility onto the buyer as if the seller has no responsibility once a sale is completed.
- Sometimes producers are few and powerful while the consumers purchase in small amounts and are scattered. Big companies with huge wealth manipulate the market in many ways.
- At times false information is passed on through the media, and other sources to attract consumers. For example, a company for years sold powder milk for babies all over the world as the most scientific product claiming this to be better than mother’s milk. It took years of struggle before the company was forced to accept that it had been making false claims. Similarly a long battle was fought with the cigarette manufacturing companies to accept that their product could cause cancer. Hence there is a need for rules and regulations to ensure protection for consumers.
Question 2: What factors gave birth to the consumer movement in India? Trace its evolution?
Answer:
The factors that gave birth to the consumer movement in India are manifold. It started as a “social force” with the need to protect and promote consumer interests against unfair and unethical trade practices. Extreme food shortages, hoarding, black marketing and adulteration of food led to the consumer movement becoming an organised arena in the 1960s. Till the 1970s, consumer organisations were mostly busy writing articles and holding exhibitions.
More recently, there has been an upsurge in the number of consumer groups who have shown concern towards ration shop malpractices and overcrowding of public transport vehicles. In 1986, the Indian government enacted the Consumer Protection Act, also known as COPRA. This was a major step in the consumer movement in India.
Question 3: Explain the need for consumer consciousness by giving two examples.
Answer:
Two examples are Reji’s suffering and Amritha’s waiting. In case of Reji, a hospital, due to negligence of the doctors and staff in giving anaesthesia, crippled him for life. In case of Amritha, an engineering graduate, after attending an interview for job, did not receive any news of the result. In both the cases, they were conscious of their rights. Reji’s father filed a complaint in the State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission claiming compensation of ? 5 lakh for medical negligence and deficiency in service.
The State Commission dismissed his case but he appealed again in the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission, New Delhi. The National Commission in its decision held hospital responsible for medical negligence and directed to pay the compensation. In case of Amritha, she filed an application under RTI Act to know the result. She soon got her call letter for appointment. Thus, there is a need for consumer consciousness to protect their interests successfully.
Question 4: Mention a few factors which cause the exploitation of consumers.
Answer: Exploitation of consumers is caused by a variety of factors. Producers are always looking for easy ways to increase profits. Adulterated or low-quality goods have fewer production costs, and if the consumer is unaware or illiterate, it is easy to cheat him/her. Also, shopkeepers brush off their responsibility by claiming that the manufacturer is to blame. Consumers feel helpless in this situation. Often, when the consumers are known not to check the retail price of a commodity on its packing, sellers add extra charges to the same. In places where there is no awareness of consumer rights and the COPRA, consumer exploitation is rampant.
Question 5: What is the rationale behind the enactment of Consumer Protection Act 1986?
Answer:
The rationale behind the enactment of Consumer Protection Act 1986 (COPRA) was to protect the interests of the consumers because there are no legal formalities for filing the complaint. A consumer need not employ a lawyer or professional for legal assistance. He himself can plead the case in a consumer court. A person can make a complaint to consumer court on a plain paper along with supporting documents such as guarantee or warrantee card, cash memo etc.
Question 6: Describe some of your duties as consumers if you visit a shopping complex in your locality.
Answer:
Some of my duties as a consumer if I visit a shopping complex include checking expiry dates of the products I wish to purchase, paying only the maximum retail price printed on the goods, preventing shopkeepers from duping me with defective products, and registering a complaint with a consumer forum or court in case a seller refuses to take responsibility for an adulterated or flawed product.
Question 7: Suppose you buy a bottle of honey and a biscuit packet. Which logo or mark you will have to look for and why?
Answer:
While buying a bottle of honey or a biscuit packet, the logo or mark one will have to look for is ISI or Agmark. These are logos certifying the quality of goods in the market. Only those producers are allowed to use these marks who follow certain quality standards set by the organisations issuing these certifications. Thus, if a bottle of honey or a biscuit packet has one of these logos on it, then it implies that the product is of good quality.
Question 8: What legal measures were taken by the government to empower the consumers in India?
Answer:
The following legal measures were taken by the government to strengthen the consumers in India :
- Consumer Protection Act popularly known as COPRA was enacted in 1986. It was amended in 1991 and 1993.
- In October 2005, Right to Information Act was enacted. This enables citizens to have all the information about the functions of government departments. The citizens have the right to know the particulars of goods and services they purchase.
Question 9: Mention some of the rights of consumers and write a few sentences on each?
Answer:
Some of the rights of consumers include the right to be informed, the right to choose, the right to seek redressal and the right to representation in consumer courts. Under the RTI Act of 2005, consumers can now even get information regarding the working of government departments. The right to choose allows a consumer to choose if he wishes to continue or discontinue the use of a service he purchased. The right to seek redressal permits a consumer to complain against unfair trade practices and exploitation.
Question 10: By what means can the consumers express their solidarity?
Answer:
The consumers can express their solidarity by forming consumer awareness organisation which may get representation in various committees formed by the government. There should be consumer’s active involvement to protect the interest of all the consumers.
Question 11: Critically examine the progress of the consumer movement in India?
Answer:
The consumer movement in India has evolved vastly since it began. There has been a significant change in consumer awareness in the country. Till the enactment of COPRA in 1986, the consumer movement did not bear much force, but ever since its inception, the movement has been empowered substantially. The setting up of consumer courts and consumer groups has been a progressive move. However, in contemporary India, the consumer redressal process is quite complicated, expensive and time-consuming. Filing cases, attending court proceedings, hiring lawyers, and other procedures make it cumbersome. In India, there are over 700 consumer groups of which, unfortunately, only about 20-25 are well-organized and functioning smoothly.
Question 13: Say True or False.
- COPRA applies only to goods.
- India is one of the many countries in the world which has exclusive courts for consumer redressal.
- When a consumer feels that he has been exploited, he must file a case in the District Consumer Court.
- It is worthwhile to move to consumer courts only if the damages incurred are of high value.
- Hallmark is the certification maintained for standardisation of jewellry.
- The consumer redressal process is very simple and quick.
- A consumer has the right to get compensation depending on the degree of the damage.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which one of the following logos is used for standardisation of agricultural products?
(a) I.S.I
(b) Hallmark
(c) Agmark
(d) ISO
2. In which one of the following courts a consumer should file a case if he/she is exploited in the market?
(a) Local court
(b) State court
(c) Supreme court
(d) Consumer court
3. Hallmark is used as a logo for which one of the following?
(a) Agricultural products
(b) Jewellery
(c) Electrical goods
(d) Electronic goods
4. On which one of the following items is I.S.I. used as a logo?
(a) LPG Cylinder
(b) Jewellery
(c) Gold
(d) Agricultural products
5. For which of these products does it become mandatory for the producer to get certified?
(a) Fruits
(b) Telephones
(c) LPG Cylinders
(d) Cigarettes
6. The district court deals with the cases involving claim up to …………..
(a) ₹ 1 crore
(b) ₹ 40 lakhs
(c) ₹ 30 lakhs
(d) ₹ 20 lakhs
7. The district level consumer court deals with the cares involving claims
(a) upto 20 lakhs
(b) upto 15 lakhs
(c) upto 1 crore
(d) upto 25 lakhs
8. Which of the following rights related to availing details of ingredients of a product?
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to choose
(c) Right to be informed
(d) Right to represent
9. In which one of the following years was the Right to Information Act Implemented?
(a) 2004
(b) 2005
(c) 2006
(d) 2007
10. The district level court deals with the cases involving claims:
(a) upto ₹10 lakhs
(b) upto ₹20 lakhs
(c) between ₹20 lakhs to ₹1 crore
(d) exceeding ₹1 crore
11. When did the United Nations adopt the guidelines for consumer protection?
(a) 1983
(b) 1984
(c) 1985
(d) 1986
12. Which one of the following statements is false?
(a) The consumer has a right to represent in the Consumer Court.
(b) The consumer redressal process is very simple and very quick.
(c) Hallmark is the certification maintained for standardisation of jewellery.
(d) The consumer has the right to be informed.
13. In the market place rules and regulations are required for the protection of the
(a) Sellers
(b) Suppliers
(c) Consumers
(d) Owners
14. In India, the consumer movement as a ……………….. originated with the necessity of protecting and promoting the interests of consumers against unethical and unfair trade practices.
(a) Cultural force
(b) Social force
(c) Economic force
(d) Political force
15. Rampant food shortages, hoarding, black marketing gave birth to the consumer movement in an organized form in the year
(a) 1947s
(b) 1970s
(c) 1960s
(d) 1965s
16. At International level, this has become the foundation for the consumer movement
(a) Consumers International
(b) COPRA
(c) Consumers Forum
(d) None of the above
17. A major step taken in 1986 by the Indian government was the enactment of
(a) RTI Act
(b) Consumer Protection Act.
(c) Consumer Movement
(d) Consumer Courts
18. In case of Reji Mathew, he suffered due to improper anesthesia which resulted in brain abnormalities. Who was held responsible by the National Commission after locking into a complaint ?
(a) Father
(b) Mother
(c) Hospital
(d) Patient himself
19. Because of this right, rules have been made so that the manufacturer displays all the information relating to the commodity
(a) Right to choose
(b) Right to be heard
(c) Right to seek redressal
(d) Right to be informed
20. In October 2005, the Government of India enacted a law known as
(a) Right to Choose Act
(b) Right to Information Act.
(c) COPRA
(d) Public Distribution System
21. A student who has paid lumpsum fee for course of three years to a coaching institute, now decides in between to discontinue that institute due to lack of quality of teaching. Can this student get a proportionate amount of fee refunded as per the law?
(a) No
(b) Yes
(c) May or May Not
(d) None of them
22. Consumers have the right to be protected against any danger caused by goods like electrical goods and pressure cookers. The right referred here is
(a) Right to seek redressal
(b) Right to be heard
(c) Right to safety
(d) Right to consumer education
23. Manufacturer should not use aggressive selling techniques to sell a particular product without giving the consumer a chance to select from alternative products available. Which right is mentioned here?
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to choose
(c) Right to heard
(d) Right to be informed
24. Which right of consumer is violated if the consumers are not allowed to get their claims settled against the manufacturer in case they are cheated or exploited?
(a) Right to seek redressal
(b) Right to choose
(c) Right to be heard
(d) None of them
25. Consumer movement in India has led to the formation of various organizations locally known as
(a) Consumer Protection Council
(b) COPRA
(c) Resident Welfare Association (RWA)
(d) None of them
26. Consumer Forums guide consumers on how to file cases and represent individual consumers in the consumer court. Is this statement true?
(a) No
(b) May or May Not
(c) Yes
(d) Never
27. Under COPRA, a ……………. quasi-judicial machinery was set up for redressal of consumer disputes.
(a) Two-tier
(b) Three-tier
(c) Four-tier
(d) Five-tier
28. State-level court deals with the cases involving claims between
(a) ₹ 1 to 20 lakhs
(b) ₹ 1 Crore and above
(c) ₹ 20 lakhs to ₹ 1 Crore
(d) Any amount
29. Logos and certification which help consumers get assured of quality while purchasing the goods and devices are
(a) ISI
(b) Agmark
(c) Hallmark
(d) All of them
30. National Consumers’ Day in India is observed on
(a) 24 December
(b) 14 December
(c) 14 January
(d) 31 December
31. World Consumers Rights Day is celebrated on
(a) Jan 15
(b) Feb 15
(c) March 15
(d) Jan 1
32. The organization which sets standards of products at the International level
(a) ISO
(b) COPRA
(c) Agmark
(d) BIS
33. Organisation which sets International food standards
(a) Consumer International
(b) Codex Alimentarius Commission
(c) ISO
(d) COPRA
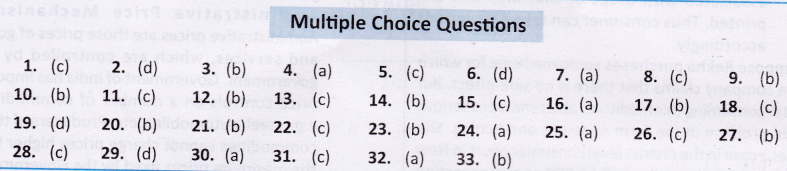
ANSWERS